How to Enhance Every Touchpoint in a Customer’s Journey
by Nicole Robinson | Published On December 23, 2023 | Last Updated May 23, 2024
.png?sfvrsn=946021e5_1)
Discover key strategies to enhance customer journeys with effective touchpoint analysis and customer experience enhancement.
Understanding customer journeys is crucial in today’s hyper-competitive business environment. Journey mapping is a tool that outlines how customers interact with a brand and greatly affects their overall experience.
The process involves analyzing every point of contact between the customer and the brand, which is key to improving the overall customer experience. Here’s what you need to know about customer journey mapping and its critical role in enhancing customer experiences through touchpoint analysis.
What is the customer journey?
A customer journey includes every experience a customer has with a company, from initial engagement through various touchpoints to the eventual outcome.
Touchpoints, the individual interactions between a customer and a brand, are pivotal in sculpting the overall customer experience. Each touchpoint, whether it's a phone call, an email, or an in-store visit, has the potential to alter a customer’s perception and decision-making process dramatically.
Understanding these journeys in their entirety allows businesses to create more engaging, satisfying, and valuable experiences for their customers. In a world where 73% of customers point to experience as an important factor in their purchasing decisions, understanding and refining these journeys is vital for any business looking to thrive.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer journey, showing the different stages, touchpoints, channels, and emotions that a customer experiences when interacting with a brand, product, or service. It can help businesses understand how their customers perceive and experience their offerings and how they can improve them to meet their needs and expectations.
8 elements of a customer journey map
A customer journey map typically includes the following 8 elements:
1. Customer persona
A customer persona is a fictional profile of a typical customer segment that describes its demographics, behaviors, motivations, goals, and pain points.
This step involves segmenting the customer base and developing detailed profiles for each segment. These personas, which go beyond just demographic sketches, are built on a foundation of behavioral insights, needs, preferences, and pain points.
Through analyzing customer data, feedback, and market research, businesses can create rich, nuanced personas that reflect the varied facets of their customer base. These personas then become the guiding light for all subsequent steps in the journey mapping process, ensuring that strategies and touchpoints are aligned with actual customer profiles.
For example, a credit union might create a persona for a young professional who is looking for a reliable and convenient financial partner. A possible persona for a credit union could look something like this:
Jessica
- Age: 28
- Occupation: Marketing manager at a tech company.
- Income: $75,000/year.
- Location: San Francisco, CA.
- Education: Bachelor's degree in business administration.
- Marital status: Single, no children.
- Personality: Ambitious, outgoing, adventurous, tech-savvy.
- Goals: To advance her career, save for a down payment, travel the world.
- Needs: A flexible and secure checking account, a high-yield savings account, a low-interest credit card, a personal loan for a vacation, online banking and mobile app access, financial advice, and education.
- Pain points: High fees and interest rates, poor customer service, lack of trust and transparency, inconvenient branch locations and hours, limited product options and features.
By creating a persona like Jessica, the credit union can better understand and empathize with their target customer segment. They can also use the persona to guide their decisions and actions in each customer journey stage, from raising awareness to retaining loyalty.
2. Customer stages
The customer journey can be divided into four main stages: awareness, consideration, decision, and retention. Each stage represents a different level of engagement and relationship between you and your customers.
Awareness:
This is the stage where customers become aware of a problem or need and start to look for possible solutions or alternatives. You can attract the customer's attention by using various marketing channels, such as advertising, social media, blogs, or referrals, and providing relevant and valuable content that educates your customers about their problems and potential solutions.
Consideration:
This is the stage where customers evaluate and compare different options or providers that can solve their problems or meet their needs. You can influence the customer's choice by offering clear and compelling value propositions, highlighting your competitive advantages, providing testimonials and reviews, or offering free trials or demos.
Decision:
This is the stage where customers make a purchase decision and complete the transaction with your business. You can facilitate the customer's decision by simplifying the checkout process, providing multiple payment options, offering guarantees/warranties, or upselling or cross-selling related products/services.
Retention:
This is the stage where customers continue to use the product or service and develop loyalty and satisfaction with your business. You can retain customers by providing excellent customer service, delivering consistent quality, soliciting feedback, rewarding loyalty, or creating a sense of community.
3. Customer actions
Customer actions are the specific activities that a customer performs at each stage of the journey, such as searching for information, comparing options, making a decision, using the product, or providing feedback. To collect customer actions, you need to understand what motivates your customers to move from one stage to another and what barriers or challenges they may face along the way.
Some methods to collect customer actions are:
Customer interviews and surveys
Asking customers directly about their actions, reasons, and difficulties can provide valuable insights into their behavior and preferences. You can use open-ended questions, rating scales, or multiple-choice options to elicit responses from customers. However, this method relies on customers' memory and honesty, which may not always be accurate or reliable.
Customer observation and ethnography
Observing customers in their natural environment, such as their home, workplace, or store, can reveal how they interact with the product or service and what triggers or influences their actions. You can capture customer actions by using video recordings, field notes, or shadowing techniques. However, this method may be intrusive, expensive, or time-consuming and may not reflect the diversity of customer segments.
Web analytics and data mining
Analyzing customer data from various sources, such as website visits, social media posts, online reviews, purchase history, or customer service calls, can provide quantitative and objective measures of customer actions. You can use tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Insights, or a CRM to track and visualize customer data. However, this method may not capture customers' underlying motivations, emotions, or pain points, or account for offline or indirect interactions.
4. Customer touchpoints
Mapping out touchpoints involves an exhaustive audit of every possible customer interaction with the brand. This includes direct interactions, such as purchases and customer service calls, and indirect ones, like social media engagement and brand mentions.
Modern CRM systems and analytics tools can track these interactions across both physical and digital realms, providing a comprehensive picture of the customer journey. This customer interaction mapping must consider the evolving nature of touchpoints, especially with the rapid digitalization of customer interactions.
The goal here is to create a complete map of each customer’s journey, highlighting every potential point of engagement, whether it be through a website visit, a mobile app interaction, an in-store experience, or a call to customer service.
Touchpoint matrix
To identify the key touchpoints, you can use the touchpoint matrix, a table that ranks each touchpoint according to two criteria: importance and satisfaction. Importance is how much the touchpoint matters to the customer, and satisfaction is how well the touchpoint meets the customer’s expectations. You can use a scale of 1 to 5 to rate each touchpoint and then plot them on a matrix like this:
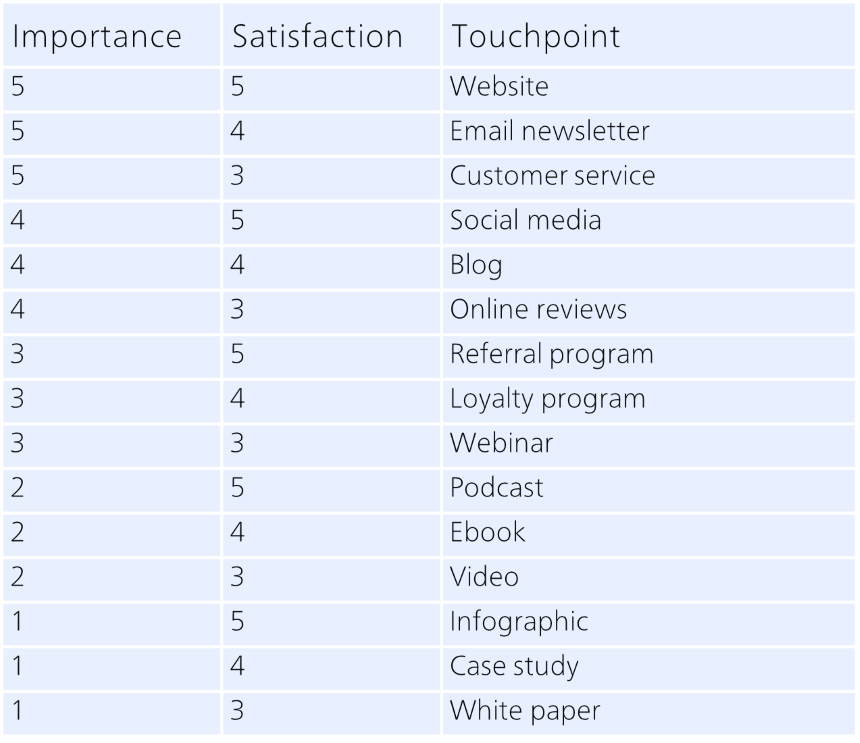
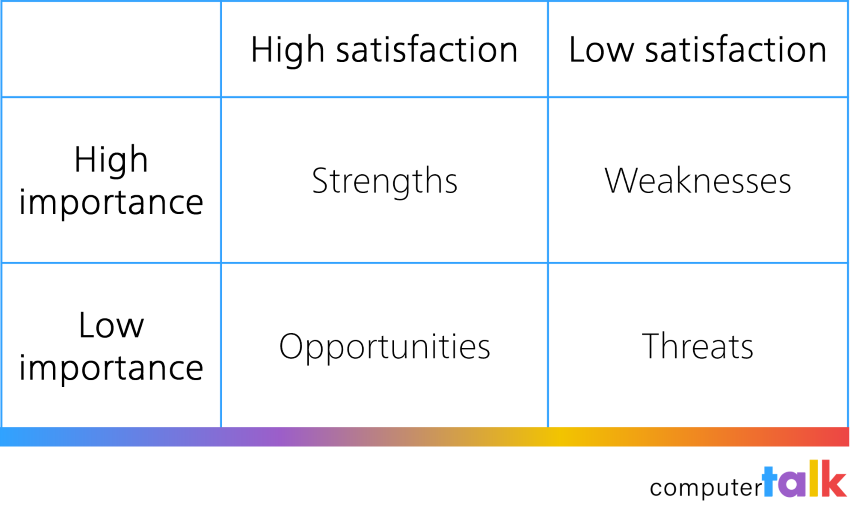
The next step is to do a SWAT analysis to discover your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. You should maintain or enhance your strengths, prioritize and improve your weaknesses, leverage and promote your opportunities, and eliminate or minimize your threats.
5. Customer channels
Customer channels are the platforms that facilitate customer interactions. These channels can be online, offline, mobile, or desktop.
One of the ways to collect information on what channels your customers are using is to conduct surveys or interviews with your existing customers. You can ask them questions such as:
- How did you find out about our product or service?
- What channels do you use to learn more about our product or service?
- What channels do you use to purchase our product or service?
- What channels do you use to get support or feedback from us?
- What channels do you prefer to use and why?
Another way to collect information on which channels your customers are using is to analyze your web analytics or CRM data. You can track metrics such as:
- The sources of traffic to your website or app, such as search engines, social media, email, or referrals.
- The behavior of visitors on your website or app, such as the pages they view, the time they spend, the actions they take, or the devices they use.
- The conversion rates of different channels, such as the percentage of visitors who complete a desired goal, such as signing up, downloading, or buying.
- The retention rates of different channels, such as the percentage of customers who come back, renew, or refer others.
By collecting and analyzing this information, you can create a customer journey map that shows the channels that your customers use at each stage of their journey, and how they interact with your business through those channels.
6. Customer emotions
Customer emotions are a crucial component of the customer journey mapping process, as they reveal how customers feel about their interactions with your business and what motivates them to take certain actions. By understanding your customers' emotions at each stage and touchpoint, you can empathize with them and design an experience that meets their emotional needs and goals.
To find out how your customers are feeling, you can use various methods and tools, such as asking the customers to rate their satisfaction, happiness, or loyalty, asking open-ended questions to elicit their thoughts and opinions, or observing their facial expressions, body language, or tone of voice. You can also use analytics tools, such as sentiment analysis, to measure the polarity and intensity of the customer emotions from their online reviews, comments, or feedback.
Customer emotions can be mapped along the customer journey using various formats, such as color coding, labels, icons, graphs, or curves. They can also be categorized into positive, negative, or neutral or more specific types, such as joy, anger, fear, surprise, or sadness.
These emotions can be used for various purposes, such as identifying the emotional peaks and valleys, the moments of truth, the wow factors, or the pain points in the customer journey. You can use the customer’s emotions to generate insights, create strategies, design products, or evaluate outcomes. They can also be used to improve the customer experience, increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, retention, advocacy, or create an emotional connection with the customers.
7. Customer pain points
One of the key aspects of customer journey mapping is to identify and understand customer pain points. Customer pain points are the problems or challenges that a customer faces at each stage and touchpoint of their journey, such as lack of information, confusion, delay, error, or dissatisfaction. Customer pain points can have a negative impact on the customer experience, satisfaction, loyalty, retention, or advocacy. They can also indicate the areas where you can improve your products, services, processes, or communication.
To identify the customer pain points, you need to collect and analyze data from various sources, such as customer feedback, surveys, reviews, complaints, analytics, observation, or interviews. You need to map the pain points along the customer journey and categorize them by type, severity, frequency, or impact. You need to prioritize your customer pain points and determine which ones are the most urgent, important, or feasible to solve.
8. Customer opportunities
The last component in the customer journey mapping process is identifying and exploring the opportunities arising from the customer pain points. Customer opportunities are the solutions or improvements that you can provide to address the customer pain points and enhance the customer experience, such as providing more information, simplifying the process, reducing the waiting time, fixing errors, or exceeding expectations. Customer opportunities can help you deliver value to your customers and achieve their goals.
How to enhance your customers’ journey

Analyze the current performance of each touchpoint
Once you have your customer journey map, it's time to analyze the current performance of each touchpoint using quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data is the numerical information that you can measure and track, such as traffic, conversions, bounce rate, retention, revenue, etc. Qualitative data is the descriptive information that you can observe and understand, such as feedback, comments, reviews, or testimonials.
To analyze each touchpoint's current performance, you need to set up key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your business goals and customer expectations. For example, if your goal is to increase sales, you might use KPIs like conversion rate, average order value, customer lifetime value, etc. If your goal is to improve customer satisfaction, you might use KPIs like net promoter score, customer satisfaction score, customer effort score, etc.
You also need to collect and analyze the data related to each touchpoint. You should look for patterns, trends, gaps, and insights that can help you understand how each touchpoint is performing and its strengths and weaknesses. You should also compare your performance with your competitors and industry benchmarks to see how you stack up against them.
Implement improvements and measure the results
The final step to enhancing every touchpoint in a customer’s journey is implementing improvements and measuring the results. Based on your analysis, you should identify the areas that need improvement and come up with some ideas and actions that can enhance the customer experience at each touchpoint. You should also prioritize the most impactful and feasible improvements and create a plan to execute them.
Some examples of improvements that you can implement are:
- Optimize your website for speed, usability, and SEO.
- Segment your email list and personalize your messages.
- Train your customer service team and provide multiple channels of support.
- Create engaging and relevant content for your social media and blog.
- Encourage and respond to online reviews and feedback.
- Offer incentives and rewards for referrals and loyalty.
- Create and promote valuable and educational resources like webinars, podcasts, ebooks, etc.
Once you implement the improvements, you need to measure the results using the same KPIs and tools that you used in the previous step. You should track and monitor the changes in performance and compare them with the baseline data. You should also collect and analyze the feedback from your customers and see how they perceive the improvements. You should then evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of your improvements and make any adjustments or refinements as needed.
Benefits of Comprehensive Customer Journey Analysis
A thorough customer journey analysis offers multiple benefits. It leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty, as businesses can fine-tune their interactions to meet customer needs better.
With this analysis, businesses can identify and rectify bottlenecks in the customer experience, directly contributing to smoother customer interactions. Additionally, optimizing touchpoints allows businesses to see a tangible increase in sales and revenue as businesses that excel in customer experience outperform others by nearly 80% in sales growth.
10 Tools for Improving Customer Journeys
Technological advancements have revolutionized the way businesses track and analyze customer journeys.
Some of the tools used for customer journey mapping include:
Customer feedback surveys: These are questionnaires that collect data from customers about their experiences, satisfaction, expectations, and suggestions. They can be conducted online, via phone, email, social media, or in person.
Web analytics: These are software applications that track and measure website traffic, behavior, conversion, and retention. They can provide valuable insights into how customers interact with the web pages, what they search for, where they drop off, and how they navigate through the site.
Heatmaps: These are visual representations of how customers interact with a website or an app. They show where customers click, scroll, hover, or tap, indicating their areas of interest, attention, and engagement.
Session recordings: These are recordings of individual customer sessions on a website or an app. They show how customers move their mouse, type, swipe, or zoom, revealing their goals, frustrations, and obstacles.
Customer interviews: These are one-on-one conversations with customers that delve deeper into their motivations, emotions, challenges, and expectations. They can be conducted face-to-face, over the phone, or via video call.
Focus groups: These are discussions with a selected number of customers exploring their opinions, attitudes, and preferences. They can be moderated by a facilitator or conducted online.
Observation: This is a technique that involves watching customers as they use a product or service in their natural environment. It can reveal how customers behave, what they need, and what influences their decisions.
Persona maps: These are visual summaries of the customer personas that highlight their key characteristics, needs, pain points, and goals. They can be created using templates, software, or paper and pen.
Journey maps: These are visual representations of the customer journey that show the stages, touchpoints, actions, emotions, and pain points of each persona. They can be created using templates, software, or paper and pen.
Empathy maps: These are visual tools that help to understand the customer's perspective by mapping out what they see, hear, say, do, think, and feel. They can be created using templates, software, or paper and pen.
Conclusion
This article discusses how to create and use customer journey maps to understand and improve the customer experience. The customer journey map can help identify the pain points, needs, preferences, and emotions of different customer personas and the opportunities and challenges for delivering value at each stage of the customer journey. We have highlighted some best practices and tips for creating effective and actionable maps to drive customer-centric innovation and business growth.
Customer journey mapping is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process that requires constant iteration and validation. By applying customer journey mapping, you can gain a deeper and more holistic understanding of your customers and align your strategies and operations with your customer needs and expectations. This can lead to improved customer satisfaction, retention, advocacy, and profitability, as well as increased competitive advantage and market share.
Interested in transforming your customer journeys? Learn more about service strategies for unmatched customer experiences.
More from our blog
 ComputerTalk is excited to announce that we have been scored as a leader in numerous categories in InfoTech Research Group’s SoftwareReviews report published in November 2022.
ComputerTalk is excited to announce that we have been scored as a leader in numerous categories in InfoTech Research Group’s SoftwareReviews report published in November 2022.
 Integrating your contact center with Microsoft Teams can provide you with an all-in-one contact center solution that is flexible and easy to use.
Integrating your contact center with Microsoft Teams can provide you with an all-in-one contact center solution that is flexible and easy to use.
 With the holidays upon us, it’s officially the season for giving! As you think about the different ways you plan on giving this year – to friends, family, or those in need – be sure to consider how you can...
With the holidays upon us, it’s officially the season for giving! As you think about the different ways you plan on giving this year – to friends, family, or those in need – be sure to consider how you can...


